Logical Data Model
Introduction
The Data Quality Framework implementation contains 7 conceptual modules:
The Users, Roles and Responsibilites
Managing users, roles and responsibilities is a fundamental aspect to ensure the proper functioning of the Data Quality Framework. This module defines the specific roles of users and their responsibilities in data quality management.
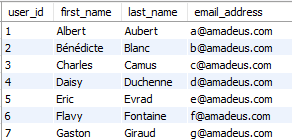
‘usr_user’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘usr_user’ table is a ‘Dimension table’
Editable: The users can be updated by a Data Engineer.

‘usr_role’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘usr_role’ table is a ‘Dimension table’
Editable: The roles can be updated by a Data Engineer.

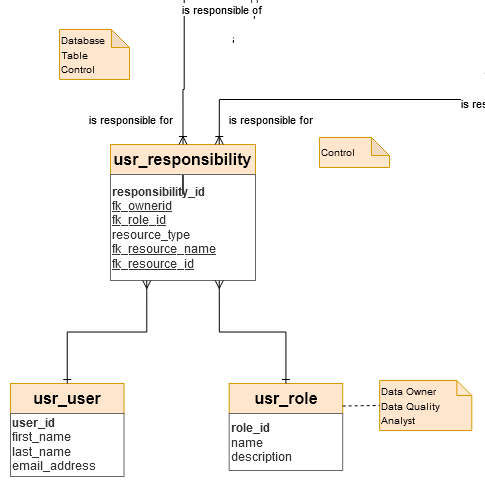
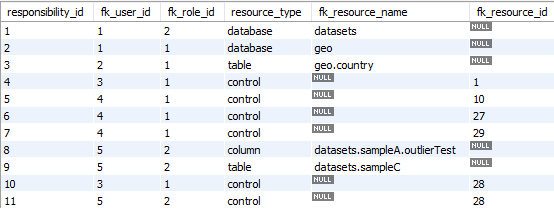
‘usr_responsibility’ table
Fact/Dimension table: N/A
Editable: The responsibilities can be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Responsibility’ in Conceptual model
The Datasets elements
As part of the Data Quality Framework implementation, dataset elements are a central module that helps structure and organize data to facilitate data management, analysis, and quality control. This module includes different types of tables and dataset elements that are essential to ensure data consistency, completeness, and integrity.
‘in_database’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘in_database’ table is a ‘dimension table’
Editable: The databases can be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Database’ in Conceptual model

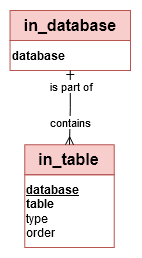
‘in_table’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘in_table’ table is a ‘dimension table’
Editable: The table’s description can be updated by a Data Engineer.
The mandatory ‘type’ attribute can take the values ‘TABLE’ or ‘VIEW’
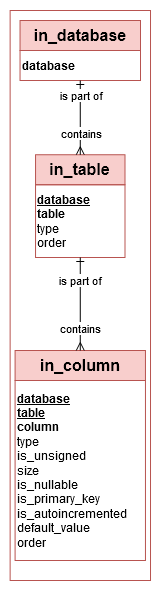
‘in_column’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘in_column’ table is a ‘dimension table’
Editable: The column’s description can be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Column’ in Conceptual model
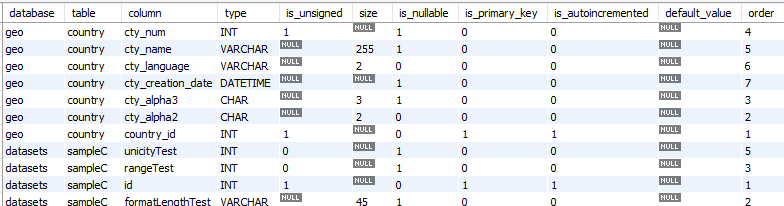
The Profiling elements
Profiling elements play a fundamental role in assessing and improving data quality within the Data Quality Framework. This module is designed to analyze data in depth, identifying trends, anomalies, and deviations from expectations. Data profiling provides a clear overview of the current state of the data, facilitating the implementation of appropriate controls.
The DQ Controls elements
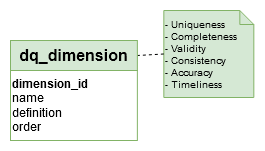
‘dq_dimension’ table
Data Quality Dimensions are measurement attributes of data, which you can individually assess, interpret, and improve. The aggregated scores of multiple dimensions represent data quality in your specific context and indicate the fitness of data for use.
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘dq_dimension’ table is a ‘Dimension table’
Editable: The dimensions can’t be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Data Quality Dimension’ in Conceptual model

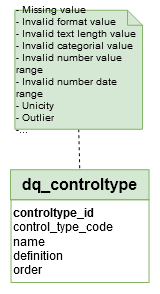
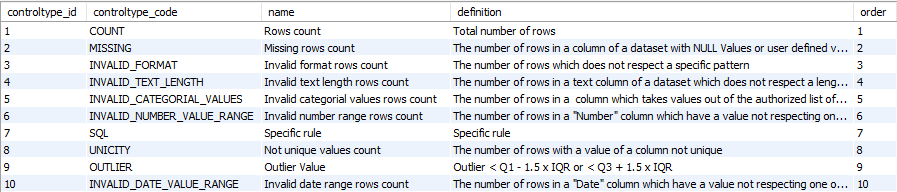
‘dq_controltype’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘dq_controltype’ table is a ‘Dimension table’
Editable: The control types can’t be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Data Quality Control Type’ in Conceptual model
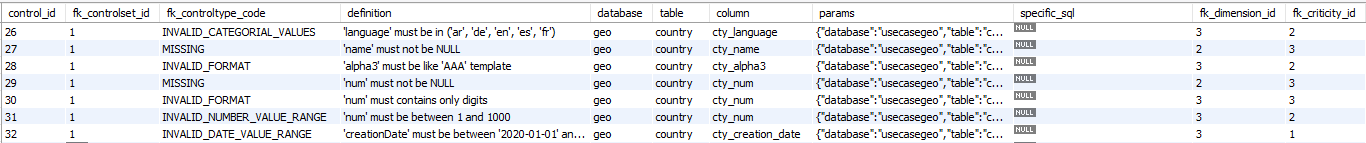
‘dq_control’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘dq_controltype’ table is a ‘dimension table’
Editable: The controls can be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Data Quality Control’ in Conceptual model
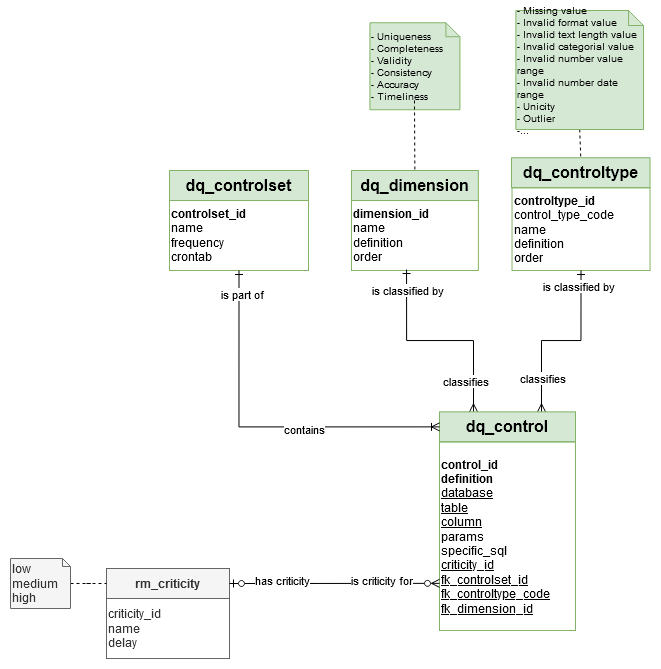
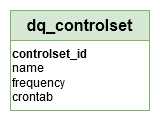
‘dq_controlset’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘dq_controltype’ table is a ‘Dimension table’
Editable: The control sets can be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Data Quality Control Set’ in Conceptual model

The DQ Control Results elements
Data Quality Control Results (DQ Control Results) elements are essential to measure the effectiveness of the quality controls implemented and to ensure continuous process improvement. This module collects, analyzes and presents the results of the various data quality checks performed on the datasets.
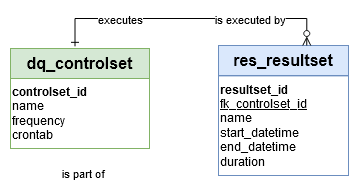
‘res_resultset’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘res_resultset’ table is a ‘Fact table’
Editable: res_resultset table can’t be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Data Quality Control Results Set’ in Conceptual model
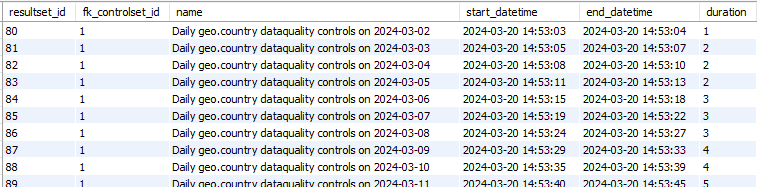
‘res_result’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘res_result’ table is a ‘Fact table’
Editable: res_result table can’t be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Data Quality Control Result’ in Conceptual model
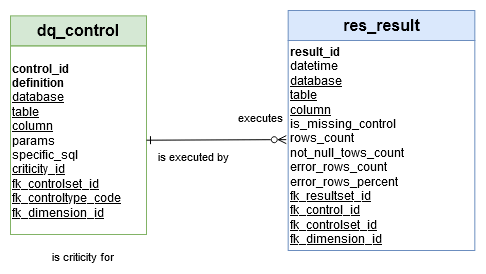
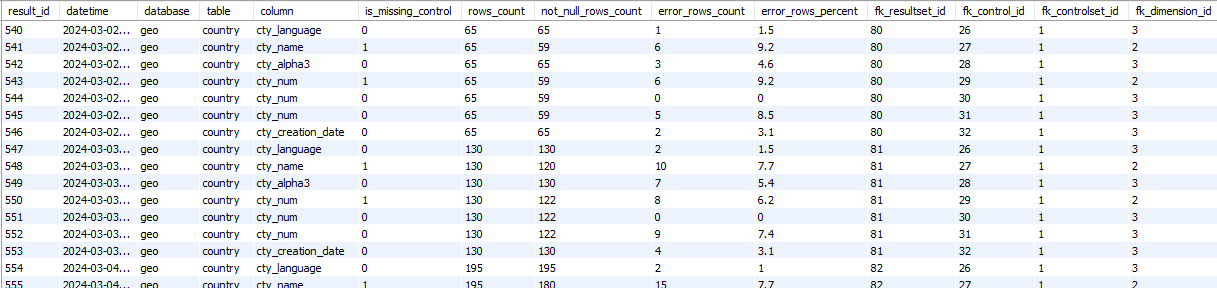
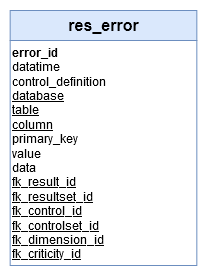
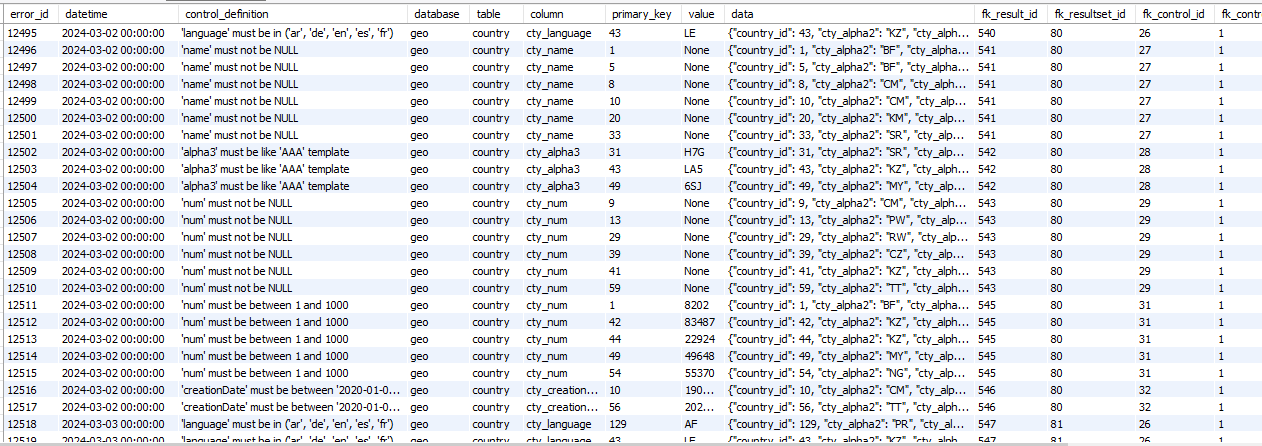
‘res_error’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘res_result’ table is a ‘Fact table’
Editable: res_result table can’t be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Data Quality Control Result Error’ in Conceptual model
The Reports elements
Report elements play a crucial role in visualizing and interpreting data related to data quality. This module allows you to generate detailed and customized reports that provide an overview of quality control results, data system performance, and remediation actions.
‘viz_threshold’ table
‘viz_color’ table
The remediation elements
Remediation elements are essential in the Data Quality Framework because they define the corrective actions to be taken when data quality issues are identified. This module is designed to ensure that anomalies, errors, and deviations from quality standards are quickly and effectively corrected.
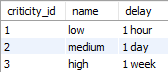
‘rm_criticity’ table
Fact/Dimension table: The ‘rm_criticity’ table is a ‘dimension table’
Editable: The controls can’t be updated by a Data Engineer.
→ ‘Data Quality Criticity Level’ in Conceptual model
‘rm_resolution’ table