Concepts
Introduction
The Data Quality Framework contains 8 conceptual modules:
Business Domains
Databases, Tables, Columns and Controls can be classified by Business Domains (HR, Marketing, Supply Chain, IT, …)
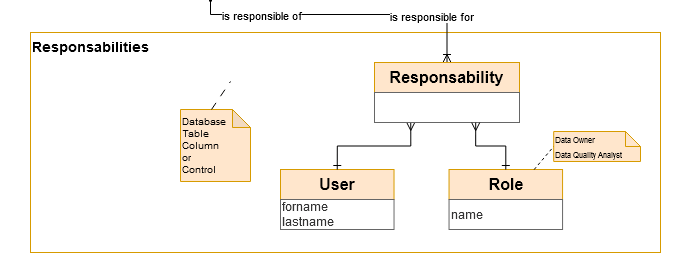
The Users, Roles and Responsibilites
Responsibilities for resources (Database, table, columns, Data Quality Control) can be assigned to certain users.
For example:
A user will have the role of ‘Data Owner’ on a database.
Another user will have the role of ‘Data Quality Analyst’ on a specific control.
Users interact with the Data Quality Engine.
For example, certain users are responsible for the quality of certain source data.
→ ‘usr_user’ table in Logical model
Interactions with the Data Quality Engine are categorized by Roles.
→ ‘usr_role’ table in Logical model
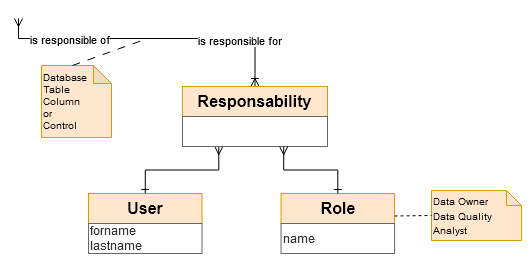
A Responsibility is the link between a User, a role and a resource (database, table, column or data quality control)
For example ‘Bénédicte Blanc’ is Data Owner of the ‘geo’ database, Gaston Giraud is Data Quality Analyst of the control #28.
→ ‘usr_responsibility’ table in Logical model
The Datasets elements
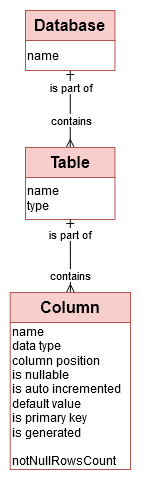
This module includes the description of all source datasets: Relational databases, tables and Columns.
A database contains many tables.
A table contains many columns.
The data sources to be qualified are available in read-only databases.
These source databases, also known as ‘Schema’, are described as “Database” within the Data Quality Engine.
→ ‘in_database’ table in Logical model

Each database includes Tables and Views.
These source tables and views, also known as datasets, are described as “Table” within the Data Quality Engine.
→ ‘in_table’ table in Logical model
Tables are structured by Columns, also known as fields.
Each column has a type (‘INT’, ‘VARCHAR’, ‘DATETIME’), can be nullable, can be part of the primary key, …
→ ‘in_column’ table in Logical model
The Profiling elements
By examining the content, both cognitively and visually, it is possible to better understand the data and highlight gaps or errors.
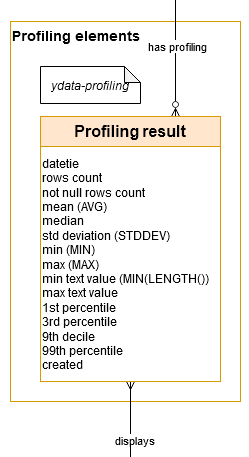
YData Profiling library sample: *
The DQ Controls elements
This module includes all the elements relating to the quality controls to be carried out.
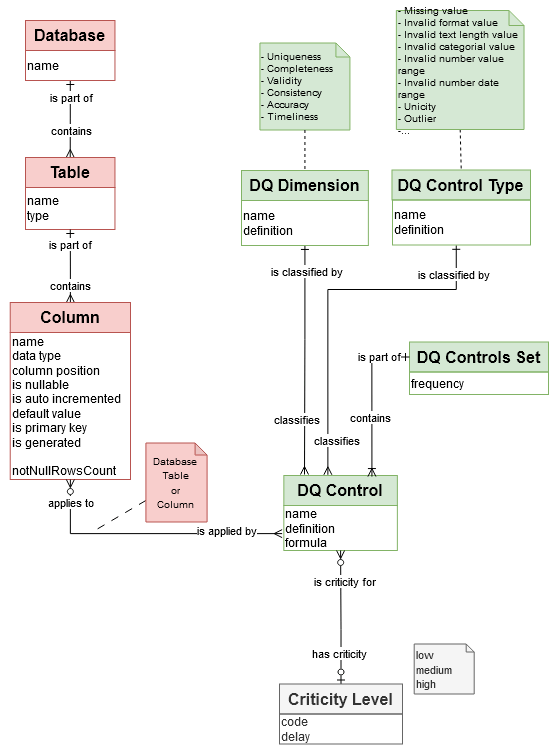
A “Data Quality (DQ) Control” is the heart of the Data Quality Engine. It describes the test that will be executed to check a quality rule.
Note
The quality rule: “The value of the date of birth of a client must be in the past”
The quality control: “The value of “dateOfBirth” in the table ‘Clients’ must satisfy the formula “value < NOW()”
→ ‘dq_control’ table in Logical model
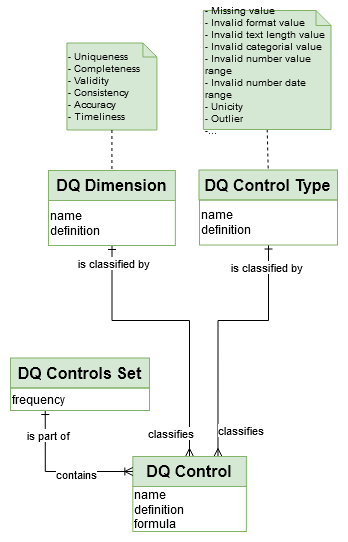
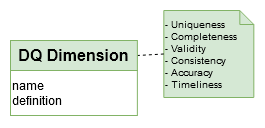
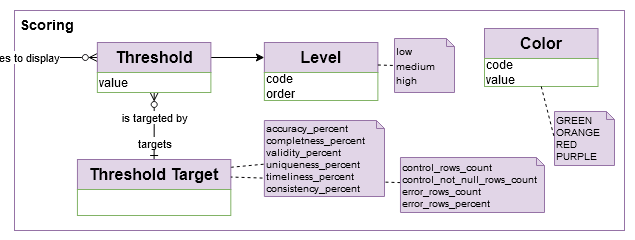
A “DQ Control” is classified by “Data Control Type”: * NULL value, * Invalid format value, * Invalid text length value, * Invalid category value, * Invalid number value range…
→ ‘dq_dimension’ table in Logical model
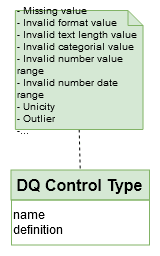
A “DQ Type” is classified by “Data Quality Dimension”: Uniqueness, Completeness, Validity, Consistency, Accuracy, Timeliness…
Summaries can be proposed based on these dimensions.
→ ‘dq_dimension’ table in Logical model
A “Data Quality Controls Set” is a collection of “Data Quality Controls” that are executed, either occasionally or periodically.
→ ‘dq_controlset’ table in Logical model

The DQ Control Results elements
When a set of controls are executed, a set of results are collected. Errors are specifically caught.
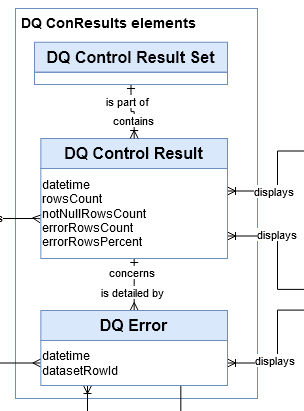
The execution of a set of controls starts on a given date and ends on another date.
→ ‘res_resultset’ table in Logical model

For each check executed, we get the number of lines tested and the number of errors found.
→ ‘res_result’ table in Logical model
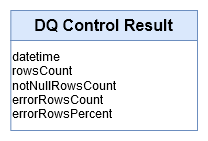
Errors are individually stored with the primary key of the row concerned, the value specifically in error and the full contents of the row.
→ ‘res_error’ table in Logical model

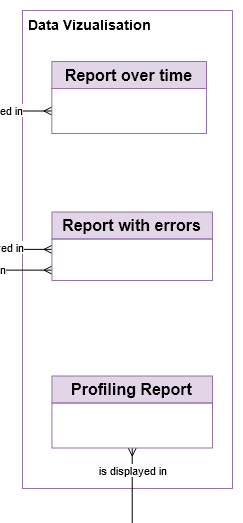
The Reports elements
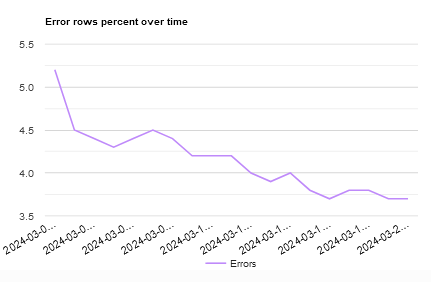
Several types of reports are made available to Data Quality Analysts: * Reports on the last result set * Reports over time * Reports with detailed errors * Profiling Report
A scoring system can be used for visualization purposes.
The remediation elements
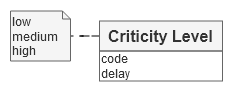
When an error is detected, depending on its criticality level, a remediation workflow can be initiated.
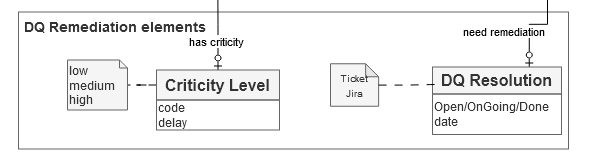
A “DQ Control” has a “Criticity level”. This criticity determines the workflow and delay of remediation of any error found.
→ ‘rm_criticy’ table in Logical model